This is a post in my So, you want to be a Product Manager? series.
As a Product Manager, the discovery process is an essential step in developing successful products that resonate with your target audience. In this post, we’ll discuss the key steps involved in product discovery, frameworks and tools that can be used in each stage, and why it’s so crucial to product management.

What is Product Discovery?
Product discovery is the foundation of product development. It’s the process of identifying a problem or opportunity, understanding its root causes, and identifying potential solutions. Product discovery involves the entire cross-functional Product team, including designers, engineers, and you! The team is responsible for conducting research, identifying user needs, and developing a deep understanding of the problem that needs to be solved.
One popular framework for product discovery is the Design Sprint, a five-day process developed by Google. The Design Sprint is a structured process that guides teams through the product discovery process, from problem identification to prototyping and testing. Other popular frameworks include the Lean Startup, which is designed to help teams develop products quickly and efficiently.
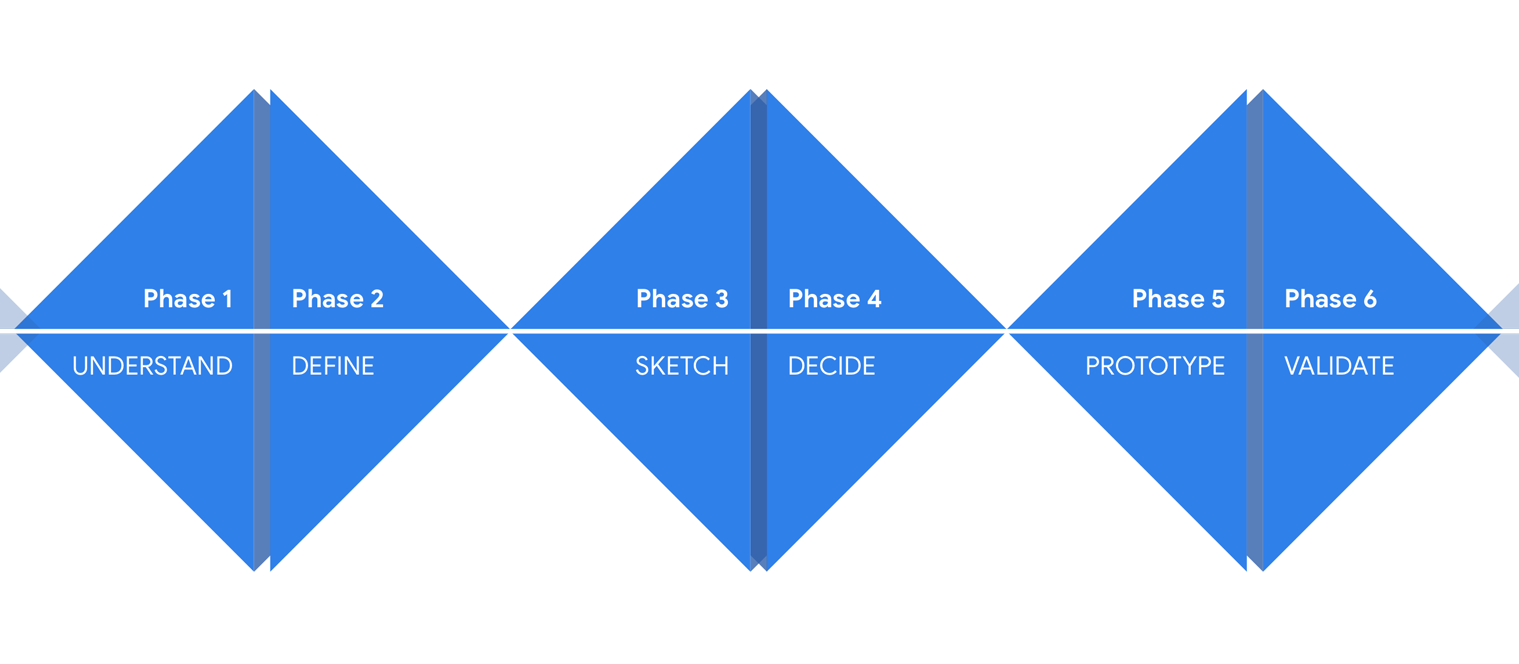
The product discovery process begins with problem identification. This is where you define the problem you’re trying to solve or the opportunity you’re looking to seize. This can be done by conducting market research, talking to customers, or analysing user and market data. Frameworks such as Jobs-to-be-Done help identify customer needs and define the problem space.

Once the problem has been identified, the team can begin to explore potential solutions. This involves ideation sessions where a range of potential solutions are generated. Tools such as mind maps, SWOT analysis, and affinity diagrams can be used to generate and organise ideas.
Once potential solutions have been identified, they need to be prioritised. This involves evaluating each solution based on its feasibility, impact, and strategic fit. The most promising solutions are then developed into a minimum viable product (MVP), which is a simplified version of the product that can be tested with users and iterated rapidly with their feedback. Tools such as the Kano Model can be used to prioritise features based on customer needs and expectations.
The MVP is tested with users to validate assumptions and iterate on the solution. Tools such as interviews, observation, A/B testing, and quantitative analytics help gather feedback and measure the success of the MVP. This feedback is used to refine the product and iterate on the solution.
Challenges in Product Discovery
While product discovery is critical to product development, there are some challenges that need to be overcome. One of the biggest challenges is ensuring that you have a clear problem definition. Don’t stop too soon! Without a clear understanding of the problem that is shared by the entire team, it’s challenging to develop a successful product. Another challenge is knowing when you have conducted sufficient research and validation. This is important to ensure that you’re building the right product for your customers. Bias or assumptions can also be a problem, so it’s essential to test assumptions and iterate quickly, allowing the date and the customer to lead the process.
Discover!
Product discovery is not a one-time event, but a continuous process. As your product evolves, you need to continuously revisit the discovery process to identify new opportunities and challenges.
Product discovery can be challenging, but by following best practices and leveraging the right tools and frameworks, you can overcome these challenges and develop successful products. If you want to be a successful Product Manager, start by mastering the art of product discovery!

Leave a Reply